How To Calculate Interest Rates – Step-by-Step Guide
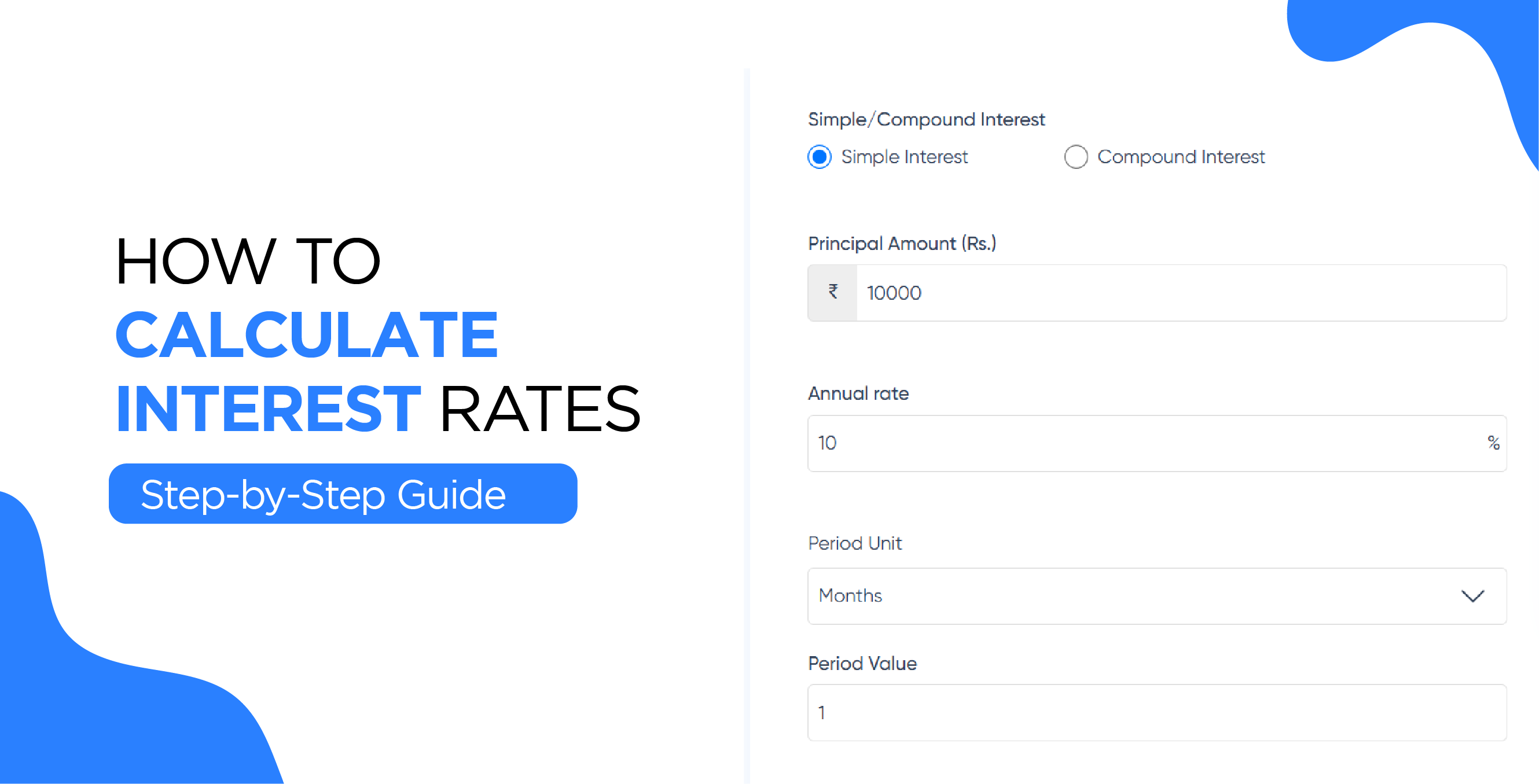
Check Your Loan Eligibility Now
By continuing, you agree to LoansJagat's Credit Report Terms of Use, Terms and Conditions, Privacy Policy, and authorize contact via Call, SMS, Email, or WhatsApp
Arvantika takes a loan of ₹1,00,000 for 2 years at 10% interest annually. She thinks she’ll pay ₹20,000 in interest (using simple interest: ₹1,00,000 × 10% × 2 = ₹20,000). But guess what? The bank compounds interest yearly, so she pays ₹21,000, not ₹20,000. Plus, there’s a ₹2,000 processing fee. That’s ₹23,000 extra!
Isn’t it wild how a small fee or calculation method can change everything?
- She forgot to check compound vs. simple interest
- Didn’t add fees
- Didn’t compare offers
- Skipped using an EMI calculator
These minor slip-ups cost her big! This blog breaks it down for you, so you don’t fall into the same trap. Let’s go!
What is The Interest Rate?
Let’s say Riya borrows ₹10,000 from a bank to buy a bicycle. The bank charges 10% interest per year. After one year, Riya has to repay ₹11,000, ₹10,000 principal + ₹1,000 interest.
Key Points:
- Interest rate is the extra amount paid or earned.
- Expressed as a percentage.
- Borrowers pay more than they borrow.
- Savers earn extra interest on deposits.
- It impacts the whole economy.
Key aspects of interest rates:
Aspect | Explanation |
Percentage | Interest rates are usually shown as a yearly percentage (Annual Percentage Rate - APR). |
Borrowing Cost | The amount a borrower pays to use money they’ve borrowed. |
Return on Investment | The money earned by savers or lenders for depositing or lending money. |
Factors Influencing Rates | Interest rates change due to things like inflation, central bank policies, demand for credit, and the economy. |
Impact on the Economy | Changes in interest rates affect spending, investing, and overall economic growth. |
What Is Simple Interest?
Let’s understand simple interest through an example of Ananya:
Ananya wants to buy a new phone but is short on cash. Her friend offers to lend her ₹10,000 at a simple interest rate of 5% per year for 2 years. Ananya agrees.
So, how much extra will she pay?
Read More - Calculate Interest Rate on Loan
Using the simple interest formula:
SI = (P × R × T) / 100
= (10,000 × 5 × 2) / 100
= ₹1,000
This means that at the end of two years, Ananya will pay back ₹11,000 — ₹10,000 as the original amount (principal) and ₹1,000 as interest.
Key Points:
- Principal (P): The original amount borrowed or invested — ₹10,000 in this case.
- Rate of Interest (R): The yearly interest rate — 5%.
- Time (T): Duration of loan or investment — 2 years.
- Simple Interest (SI): The extra money paid — ₹1,000.
- Interest stays the same each year and doesn’t compound.
Summary Table:
Component | Value |
Principal (P) | ₹10,000 |
Rate of Interest (R) | 5% per year |
Time (T) | 2 years |
Simple Interest (SI) | ₹1,000 |
Total Repayment | ₹11,000 |
What Is Compound Interest?
Let’s understand compound interest through an example.
Aarav decides to invest ₹1,000 in a savings account that offers 5% interest compounded annually. In the first year, he earns ₹50 in interest, making his total ₹1,050.
In the second year, the 5% interest is now calculated on ₹1,050, not ₹1,000. So he earns ₹52.50, and his total becomes ₹1,102.50.
This continues each year, and after 10 years, his investment grows to around ₹1,628.89 — without adding any extra money himself. That’s the power of compound interest!
Key Points:
- Interest on interest: Each year, the interest is added to the principal, so future interest earns more.
- Exponential growth: Your money grows faster compared to simple interest.
- Time matters: The longer you invest, the more you earn.
- Compounding frequency: The more often interest is compounded (yearly, monthly, etc.), the greater the growth.
Compound Interest Formula:
FV = PV × (1 + i/n)^(nt)
Where:
FV = Future Value
PV = Present Value (initial amount)
i = Annual Interest Rate
n = Number of times compounded per year
t = Time in years
Summary Table:
Year | Start Amount (₹) | Interest (5%) | End Amount (₹) |
1 | 1,000 | 50.00 | 1,050.00 |
2 | 1,050.00 | 52.50 | 1,102.50 |
... | ... | ... | ... |
10 | 1,551.33 | 77.57 | 1,628.89 |
APR vs. APY
Understanding APR and APY with an example of two friends, Meera and Raj.
Meera takes a personal loan of ₹1,00,000 from a bank. The bank tells her the interest rate is 10%, but there’s also a 2% processing fee. So, even though the interest sounds like 10%, she ends up paying ₹12,000 in total over a year. This makes the APR (Annual Percentage Rate) 12% — because it includes both the interest and the fees.
Also Read – Calculate Fixed Deposit Interest
Raj, on the other hand, opens a savings account and deposits ₹1,00,000 at an interest rate of 5% compounded monthly. Though the rate is 5%, because of monthly compounding, Raj ends up earning around ₹5,116 in a year. So the APY (Annual Percentage Yield) is 5.12%, slightly higher than the stated rate, thanks to compound interest.
Key Points:
- APR is what you pay when you borrow.
- APY is what you earn when you save or invest.
- APR includes fees; APY includes compound interest.
- APR shows the true cost of borrowing; APY shows the true return on investment.
Difference Between APR and APY
Example Summary
Person | Amount (₹) | Type | Rate | Fees/Compounding | APR/APY |
Meera | 1,00,000 | Loan | 10% + 2% fee | Fee included | 12% |
Raj | 1,00,000 | Savings | 5% comp. monthly | Compounding included | 5.12% |
APR is the cost of borrowing; APY is the gain from investing. Understanding both helps make smarter financial decisions.
Common Mistakes to Avoid:
Let’s explore common mistakes in calculating interest rates through an example.
Ravi plans to take a personal loan of ₹5,00,000 for 3 years at an interest rate of 10% per annum. Excited, he quickly signs the agreement without checking the details.
Later, Ravi is surprised when his EMI turns out to be much higher than expected. Here's what he missed:
- The bank charged a processing fee of ₹10,000, which he didn’t factor in.
- He used simple interest in his estimate, but the bank used compound interest.
- He entered the interest rate as 1.0 instead of 0.10 in his calculation — a decimal mistake!
- He didn't use an EMI calculator and had no idea about prepayment penalties.
By the time Ravi realised, he was locked into a loan that cost him significantly more.
Key Mistakes to Avoid:
- Enter the correct loan amount
- Use the right interest type (simple vs. compound)
- Include charges
- Check for prepayment terms
- Use decimal points correctly
- Always mention units (₹, %, years)
- Compare offers from multiple lenders
- Use an EMI calculator
Summary Table
Mistake | Impact |
Ignoring fees | Underestimates the true cost |
Wrong interest type | Incorrect total interest |
Decimal error | Major miscalculation |
Skipping EMI calculation | Poor budget planning |
No rate comparison | Missed cheaper loan options |
Conclusion:
Interest rates can look simple, but they affect how much you pay or earn in a big way. Always check if it’s simple or compound interest, include all fees, and use an EMI calculator. Know the difference between APR and APY. Even small mistakes can cost a lot. So, be careful, compare well, and stay alert. It’s easy once you understand it, and worth it!
FAQs:
Q1: What is the distinction between simple and compound interest?
Simple interest only calculates on the principal, but compound interest calculates on both the principal and the accrued interest.
Q2: Why isn't APR equal to the mentioned interest rate?
APR comes with additional charges, such as processing fees, giving the real price of borrowing.
Q3: What is APY on savings?
APY gives the effective annual return on savings, with the impact of compound interest.
Q4: Can charges influence the overall interest paid?
Yes, processing charges and concealed charges can make your loan repayment significantly higher.
Q5: How do I avoid interest calculation errors?
Utilise an EMI calculator, recheck rates, compare quotes, and always mention fees.
How to Guides – Investing, Trading & Wealth Building | ||
About the author

LoansJagat Team
Contributor‘Simplify Finance for Everyone.’ This is the common goal of our team, as we try to explain any topic with relatable examples. From personal to business finance, managing EMIs to becoming debt-free, we do extensive research on each and every parameter, so you don’t have to. Scroll up and have a look at what 15+ years of experience in the BFSI sector looks like.
Subscribe Now
Related Blog Post
Recent Blogs
All Topics
Contents
Quick Apply Loan
Consolidate your debts into one easy EMI.
Takes less than 2 minutes. No paperwork.
10 Lakhs+
Trusted Customers
2000 Cr+
Loans Disbursed
4.7/5
Google Reviews
20+
Banks & NBFCs Offers
Other services mentioned in this article


.png)




